For many clinicians moving into aesthetic medicine, purchasing a device can feel like a major...
.jpg?height=200&name=HCE%20HubSpot%20blog%20images%20600x350%20(65).jpg)
Advance your knowledge in the prevention, treatment and ongoing management of chronic illnesses seen in primary care.
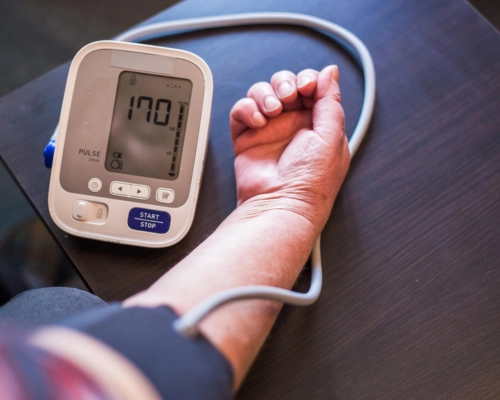
Gain the confidence to manage common chronic health issues and improve your patients’ quality of life.
- Gain a comprehensive understanding of the management of hepatitis, hypertension, coronary artery disease, obesity, PCOS, prostate cancer, and prostate conditions.
- This course is for medical doctors, International Medical Graduates, registered nurses, and degree-qualified health professionals.
- CPD-accredited and university-reviewed.
Fulfils 50 hrs for medical professionals in Australia*
100% online
$1595
Special rates available
93 hrs
Self-paced
*provided an outcome measurement activity with a minimum of 5 hours is completed.

- Provide highly sought-after interventions for chronic diseases, which affect about 58 per cent of patients and cause 90 per cent of deaths in Australia.
- Offer immediate care to patients with hypertension and cardiovascular conditions.
- Provide comprehensive care for Hepatitis A, B, and C.
- Address and prevent coronary artery disease issues.
- Manage tobacco-related health conditions in patients.
Get unlimited access to all course content, additional learning materials, ongoing post-course support, and more.
This module begins with an overview of hypertension including factors that cause inaccuracy whilst measuring blood pressure. AIHW demographics of people with high blood pressure and the modifiable and non-modifiable risk factors are supported by charts and diagrams. Suggested ways to prevent and treat hypertension include smoking cessation, healthy eating, reducing sodium and alcohol intake, supplements, regular physical activity and maintaining healthy body weight. The module then discusses the evaluation of primary and secondary hypertension and medications to avoid, and then moves to physical examinations, investigations and management of this condition. The module concludes with a case study that focuses on developing a hypertension management plan to achieve treatment goals.
This module begins with an overview of liver anatomy and physiology. The epidemiology, transmission, pathogenesis, clinical features, screening, tests, diagnosis, management, and ways to treat Hepatitis A, B and C are outlined. Clinical management of acute HBV and chronic HBV including patient support, advice on lifestyle changes, HCC screening, treatment and primary prevention of HBV infection are discussed. The initial assessment of HCV infection including DAAs, treatment regimens, side effects, renal impairment, reasons for treatment failure, advice for patients and exposure to HCV are discussed in detail.
This module provides an overview of coronary artery disease (CAD) and outlines the prevalence of the disease in Australia. It discusses the controllable and uncontrollable risk factors including using the Australian absolute cardiovascular disease risk calculator to measure these risks. Other risk factors include lifestyle measures and management of hypertension and diabetes. The diagnosis, examination, investigations and management of CAD including ongoing monitoring of this condition are outlined. The module concludes with a case study that focuses on developing a coronary artery disease management plan to achieve treatment goals.
This module begins with an overview of the epidemiology of tobacco-related conditions and statistics of deaths caused by tobacco in Australia. It briefly discusses the features of addiction, the pharmacokinetics, the different types of tobacco products and alternative tobacco and nicotine delivery methods. The module then focuses on measures to assist patients with cessation of smoking including counselling, follow-up consults, pharmacotherapy, the use of e-cigarettes as harm reduction, non-drug interventions and concomitant drugs. The health consequences of active smoking and second-hand smoke are outlined. The module concludes with different types of screening to conduct for smoking-related conditions including those affecting the lung and heart.
This module outlines the prevalence of obesity in the Australian female population, the impact of obesity on their health and wellbeing, and suggests best practice principles in formulating management plans for these patients. Obesity is defined and diagnostic guides provided. The role of the GP is outlined including primary prevention, education and understanding the drivers of obesity. Medical complications are considered. Consultation and examination/investigation guides in addition to tools and information to motivate patients for lifestyle change are included. Medications and surgery options are discussed.
This module examines the prevalence, presenting symptoms, contributing factors and underlying problems associated with PCOS. Common features, risk factors and indications for further investigation to diagnose this condition are outlined. The module offers a framework for applying the diagnostic criteria for PCOS including presenting symptoms, specific criteria for diagnosis and the process for eliminating other potential causes and conditions to optimize the health of women undergoing treatment for PCOS. Tools and resources for screening and management of the condition are also included. The module concludes by outlining symptoms of complications to look for and provides instructions for detection and management of these symptoms.
This module examines the role of the prostate and what may happen when it is not functioning normally. This includes symptoms, underlying problems and other common features associated with prostate conditions. It covers benign prostatic enlargement and associated urinary incontinence in men. Conditions that are best referred to a urologist are covered including what treatment options may be considered by the urologist which is helpful for the treating medical practitioner to know. How to establish an initial assessment for various conditions are outlined. Planning a prostate check by digital palpation, what to look for and how to interpret the pathology results are included in unit two. Charts, graphs, studies and diagrams assist with determining the appropriate management.
This module follows on from the ‘Prostate conditions and prostate checks’ module and focusses on prostate cancer. Topics include symptoms for prostate cancer, diagnosis tools including PSA and digital examination, when to refer and what information to include when referring. Understanding the function and levels of PSA testing is a feature of unit one in addition to outlining prevention studies and men at higher risk. Management of localized prostate cancer including surveillance vs surgery is discussed. Unit two includes information and studies on radiation, neoadjuvant and adjuvant RT therapies, medications, post treatment surveillance and biochemical recurrence after treatment. Unit three discusses metastatic prostate cancer and androgen deprivation therapy, androgen resistance and treatment options. Rare subtypes are covered in addition to bone health and the effects of treatment on the skeleton. The module finishes with an outline of future directions.
This module looks at ways to maintain cardiovascular health and prevent heart disease. It also outlines ways to maintain weight control and prevent obesity. Graphs and charts are used to demonstrate the effects of exercise on men. The relationship between obesity in Australia and chronic conditions is outlined including metabolic syndrome. Treatment options for obesity include lifestyle, medications, surgery and counselling. Assessment of a patient’s symptoms, recognising and managing behavioural change techniques, recognising masculinity and motivating patients are a feature of unit two. The impact of age-related sarcopenia is discussed in unit three and the challenges this presents for the obese male. Information and statistics about the effects of exercise and nutrition complete this module.

Associate Professor of Epidemiology (Chronic Diseases)
A/Prof Nicola Hawley is an Associate Professor of Epidemiology (Chronic Disease) and Anthropology at the Yale School of Public Health. Her expertise is in the aetiology and prevention of obesity-related chronic disease in resource-poor, low-income settings. Her research focuses predominantly on Pacific Islander populations, although she has ongoing collaborations in South Africa, Uganda, Honduras, China, Columbia and the US.
Methodologically, A/Prof Hawley employs a life-course approach that utilises cross-sectional, cohort, and randomised controlled trial designs to address questions of causality and identify critical periods of susceptibility. She is a mixed-methods expert and an advocate for community-engaged approaches to research, intervention, and development of health policy.
A/Prof Hawley’s current research focuses broadly on: (1) understanding how maternal and child health are impacted by rising levels of obesity and diabetes in resource-poor settings; (2) determining how innovations in healthcare delivery can impact identification and treatment of obesity-related disease during the perinatal period; and (3) developing interventions focused on pregnancy, childhood, and adolescence to prevent the intergenerational transmission of obesity-related disease.

Associate Professor Darren Katz is a urological surgeon who serves as Medical Director of Men’s Health Melbourne. He is a very approachable urologist who understands the importance of providing patients with the highest standards of multi-disciplinary care. His aim is to deliver prompt, ready-access to all forms of urological management – either elective or emergency - and is available 24/7 to GPs and patients.
A/Prof Katz is the current Leader of the Andrology Special Advisory Group for the Urological Society of Australia and New Zealand. He graduated from Melbourne University Medical School in 2001 and completed his urological training with the Royal Australasian College of Surgeons. He has spent two years at world-leading hospitals - Memorial Sloan-Kettering Cancer Center and Weill-Cornell Medical Centre - in New York completing sub-speciality urological fellowships in andrology, urological prosthetics, male voiding dysfunction, incontinence, and male infertility.
A/Prof Katz is the director of the only Australian Prosthetic and Micro-surgical Fellowship which trains overseas urologists in world-leading procedures and operations. A/Prof Katz has trained urologists from USA, Canada, Israel, and England. These urologists spend one year with A/Prof Katz and his colleagues learning about the latest treatments and operations in his field of focus.
A/Prof Katz is heavily involved with research and academics and has been awarded both national and international grants and scholarships. He has been an invited faculty member for numerous urological workshops to teach other urologists and training urologists about the latest surgical techniques. He often presents at major international conferences. He is the author of multiple peer-reviewed journal articles and serves as a reviewer for the Journal of Urology, British Journal of Urology International, Andrology, Asian Journal of Urology, Journal of Sexual Medicine, The Asian Journal of Andrology, and the Journal of Andrology and Gynaecology: Current Research. He is involved with several clinical trials and provides the most up-to-date, evidence-based treatments for his patients.
A/Prof Katz is a member of the Urological Society of Australia and New Zealand, The Fertility Society of Australia, The American Urological Association, The European Association of Urology, and The Sexual Medicine Society of North America.

Dr Christine Ahern has worked as a general practitioner in rural NSW since 1983, often with Aboriginal and Torres Strait Islander communities. Her special interests include women’s health and education.
Dr Ahern is a senior lecturer at Sydney University and has previously been the Director of Training for North Coast GP Training. In 2011 she was named the General Practice Education and Training Medical Educator of the Year, a prestigious national award. Dr Ahern holds a MBBS and FRACGP.
.png?width=143&height=143&name=Divyanshu%20Dua%20(1).png)
Dr Divyanshu Dua has worked as a Consultant Medical Oncologist at the Canberra Region Cancer Services since July 2016. He previously worked as a Staff Specialist in Medical Oncology in rural Victoria.
Dr Dua’s experience and training in medicine and oncology spans across three continents including Asia, Europe, and Australia. He specialises in lung cancers, thoracic malignancies, and genitourinary malignancies. He has a special interest in cancer in geriatric patients and a keen interest in medical services development and hospital management.
After doing most of his physician training in Adelaide, Dr Dua went on to do a clinical fellowship at the Guys Hospital in London in drug development, early phase clinical trials, and thoracic malignancies.
In his spare time, Dr Dua is a sports fan and enjoys watching and playing cricket.
.png?width=143&height=143&name=Joe%20Kosterich%20(3).png)
Dr Kosterich writes for numerous medical and mainstream publications and is a regular on radio and television. He is often called to give opinions in medico legal cases, is clinical editor of Medical Forum Magazine, adjunct professor (teaching) at UWA and a lecturer at Curtin Medical School.
Medical Advisor to Medicinal Cannabis company Little Green Pharma and Chairman of Australian Tobacco Harm Reduction Association, Dr Kosterich has self-published two books: Dr Joe’s DIY Health and 60 Minutes To Better Health, and maintains a website and blog with health information and commentary.
Previously he held senior positions in the Australian Medical Association and sat on numerous industry and government boards. He has extensive corporate experience in the setting up and management of medical centres and in helping businesses maintain a healthy workforce.
Through all this he continues to see patients as a GP each week.


Family & Bariatric Physician - Board Certified
AOBFP & ABOM
Dr Brad Lipson is a family medicine expert in Boca Raton, Florida.
Dr Lipson is an alumnus of Nova Southeastern University in Fort Lauderdale, Florida, with a doctorate in osteopathic medicine (D.O.) after graduating from the University of Miami with a B.S. in psychobiology and minor in business administration. He completed training as chief resident at the family practice residency program at Wellington Regional Medical Center in Wellington, Florida. He received his family practice board certification from the American Osteopathic Board of Family Physicians. He is affiliated with the American Osteopathic Association, American College of Osteopathic Family Practitioners, and the Florida Osteopathic Medical Association.
Dr Lipson was born and raised in South Florida; he is married with two children, speaks Spanish, and enjoys Asian culture, geography, and computer technology. His interests include heart attack and stroke prevention, diabetes (diabetology), cholesterol (lipidology), obesity / metabolic syndrome, high blood pressure, men's health, and sleep disorders. He is a board certified family physician. Fellow of the American Society for Preventative Cardiology.

$1595
*provided an outcome measurement activity with a minimum of 5 hours is completed.
Bundle two courses and save 5%, or three courses and save 10% upon enrolment.
Talk to us about deferred payment options, registrar scholarships and special rates.
*For Australian residents only: Online course prices are shown exclusive of GST. If you are GST-registered, please enter a valid ABN at checkout to ensure GST is not applied. Otherwise, 10% GST will be added at checkout. View our FAQ for more information.


HealthCert courses have become the standard by which you gauge all others.
Dr K. Abolarinwa
Good courses with excellent speakers. I particularly enjoyed the case study scenarios which helped to integrate the knowledge gained.
Dr A. Tucker
This is the pathway to improve your confidence and evolve into the GP you aspire to be.
Dr S. Shinwari
| RACGP Activity Number | ACRRM Activity Number | Activity Title | Education Hours | Performance Hours | Outcome Hours | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 442742 | 38231 | Tobacco related conditions | 442742 | 38231 | 4 | 6 | 0 |
| 442722 | 38229 | Hepatitis A, B and C | 442722 | 38229 | 4.5 | 6 | 0 |
| 455707 | 38377 | Polycystic Ovarian Syndrome | 455707 | 38377 | 4.5 | 6 | 0 |
| 477057 | 38425 | Prostate conditions | 477057 | 38425 | 4 | 6 | 0 |
| 477117 | 38427 | Prostate cancer | 477117 | 38427 | 3.5 | 6 | 0 |
| 442714 | 38228 | Hypertension | 442714 | 38228 | 4.5 | 6 | 0 |
| 442738 | 38230 | Coronary Artery Disease | 442738 | 38230 | 4.5 | 6 | 0 |
| 469408 | 38403 | Obesity & Overweight Management | 469408 | 38403 | 4 | 6 | 0 |
| 479882 | 38483 | Cardiovascular health and weight control in men | 479882 | 38483 | 5.5 | 6 | 0 |
| 809337 | 38239 | Coronary Artery Disease Outcome Improvement Activity | 809337 | 38239 | 0 | 0 | 8.5 |
| Total hours | 39 | 54 | 8.5 | ||||
View the CPD Hours for all HealthCert Education activities.
The purpose of outcome measurement activities is to improve your clinical confidence in managing an identified learning gap. Outcome measurement activities are not a requirement of our Professional Certificate of Advanced Certificate courses; they are a requirement for Australian CPD purposes.
HealthCert Education provides a variety of outcome measurements activities to suit your needs:
The Advanced Certificate of Chronic Disease & Conditions is for degree-qualified medical professionals who wish to learn how to improve patient outcomes, especially those patients with chronic health issues commonly seen in general practice. This qualification is the second stage of the Professional Diploma of Chronic Disease & Conditions pathway.
This course is for medical doctors, International Medical Graduates, registered nurses, and degree-qualified health professionals. The prerequisite for this Advanced Certificate course is the successful completion of the HealthCert Professional Certificate of Chronic Disease & Conditions (or a qualification deemed equivalent).
Participants do not have to pass an IELTS test but, as the courses are delivered in English, proficiency in listening, reading and writing English is assumed.
Participants will require access to a computer/laptop, an internet connection and a basic level of technology proficiency to access and navigate the online learning portal.
Participants who have successfully completed the modules on prostate conditions & checks and prostate cancer in the Professional Certificate of Men’s Health, Polycystic Ovarian Syndrome (PCOS) in the Professional Certificate of Women’s Health, or obesity in the Advanced Certificate of Women’s Health will be granted recognition of prior learning (RPL) for these modules, thereby reducing the cost of this course and the time needed to complete it. Please ask a HealthCert Education Advisor for more details.
Further professionally recognised qualifications and prior studies may be recognised for entry into this course if the learning outcomes match exactly. Please ask a HealthCert Education Advisor for an individual assessment of your prior qualifications and experience.
This certificate course meets the minimum 50 hours CPD annual requirement across all three mandatory CPD activity types, provided an outcome measurement activity with a minimum of five hours is completed. You may use an optional HealthCert outcome measurement activity or develop your own.
Outcome measurement activities are not a requirement of Professional or Advanced Certificates.
Upon successful completion of the course requirements, course participants will receive the Advanced Certificate of Chronic Disease & Conditions and CPD hours.
This certificate course:
To learn more about the delivery of certificates in Australia and overseas, please visit our FAQs.
Professional Diploma Pathway
This course is the second stage of the three-part professional diploma pathway. The full pathway is Professional Certificate of Chronic Disease & Conditions, Advanced Certificate of Chronic Disease & Conditions, and Professional Diploma of Chronic Disease & Conditions.
This organisation is an RACGP-accredited CPD provider under the RACGP CPD Program.




Don't see your question? Explore other faqs or talk to us.
Fees will vary based on the program and study option selected (fully online vs online + optional practical workshop). Payments can be made upfront or in monthly instalments. Special rates and various payment options are available. GP registrars and doctors in training enjoy a scholarship of up to $500. Talk to us to learn more.
Completion of any HealthCert course or attendance at an event will enable you to access the HealthCert Alumni Program which includes:
HealthCert Education is pleased to issue digital credentials for alumni. Digital credentials are a permanent online record of your successful completion of a HealthCert course and are issued to all course participants in addition to PDF certificates. If you are based in Australia, you also have the option to order a hard copy of your digital certificate for a small additional fee.
The recommended study duration of this certificate course is 40.5 hours, which includes study of the pre-course activities and readings, online lectures, live tutorials, and online assessment. This self-paced course offers the flexibility of 100% online study in your own time, at your own pace, in your own home or office, with no mandatory face-to-face requirements. You are not required to be online at specific times but can view and replay video lectures at your convenience.
All HealthCert courses meet World Federation of Medical Education standards. This certificate course qualifies for CPD hours from the Royal Australian College of General Practitioners (RACGP) and the Australian College of Rural and Remote Medicine (ACRRM) in Australia. It is recognised by the Royal New Zealand College of General Practitioners (RNZCGP) in New Zealand. It is recognised by the Hong Kong College of Family Physicians (HKCFP) in China. It is a self-submitted activity in Dubai and the United Kingdom. It is a self-submitted activity through the College of Family Physicians in Canada. If you live or work outside one of the above-mentioned countries, please contact us on admin@healthcert.com to discuss whether this course can be recognised in your country.
Want to stay up-to-date with the latest case studies, podcasts, free video tutorials and medical research articles pertinent to primary care?
Our Education Advisors can assist you with any queries and tailor our education pathway to suit your current expertise, interests and career goals.